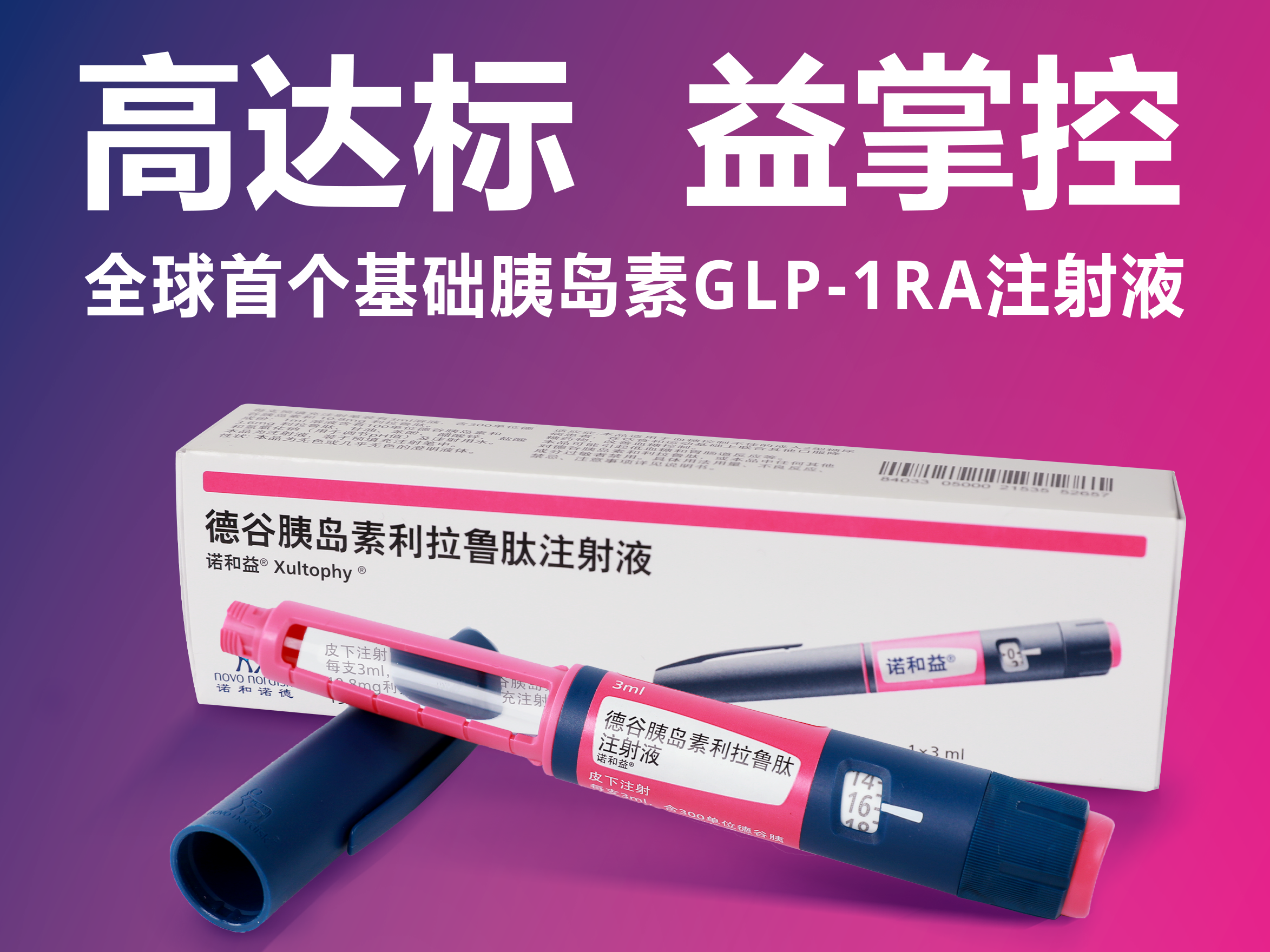
诺和益® 畅充 Xultophy® flextouch
展商: Novo Nordisk
原产国/地区:丹麦
成份:德谷胰岛素和利拉鲁肽 (采用重组DNA技术,利用酿酒酵母制成)。1ml溶液含有100单位德谷胰岛素和3.6 mg 利拉鲁肽。辅料:甘油、苯酚、醋酸锌、盐酸(用于调节pH值)、氢氧化钠(用于调节pH值)、注射用水。 适应症:用于治疗血糖控制不佳的成人2型糖尿病患者,在饮食和运动基础上联合其他口服降糖药物改善血糖控制。 用法:本品每日一次皮下注射给药。可在一天中的任何时间进行给药(最好在每天相同时间给药),不受进餐影响。
展品详情
产品:诺和益®(德谷胰岛素利拉鲁肽注射液)
介绍:
本品是全球首个基础胰岛素胰高糖素样肽-1(GLP-1)受体激动剂注射液,也是糖尿病领域首个新型生物制剂联合药物。2021年10月获得中国食品药品监督总局批准上市,11月作为“进博宝宝”在进博会首展。2022年3月诺和益® 中国商业上市,已被写入《中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2020年版)》1。2024年被《中国老年糖尿病诊疗指南(2024版)》推荐为非胰岛素治疗失效后一级推荐用药之一。
本品突破性融合德谷胰岛素和利拉鲁肽的优势,同时作用于双受体——胰岛素受体和GLP-1受体,协同互补、靶向调节,临床治疗上实现89.9%的患者血糖达标,低血糖风险低且体重获益明确。2~5本品每日一次皮下注射,可在一天中的任何时间进行给药,不受进餐时间影响。2 中国获批的适应症是:用于治疗血糖控制不佳的成人2型糖尿病患者,在饮食和运动基础上联合其他口服降糖药物改善血糖控制。2
Product: Xultophy® (Insulin Degludec and Liraglutide injection)
Introduction:
It is the worldwide FIRST innovative combination of a long-acting basal insulin and glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, also the first biological combination in diabetes industry. Xultophy® was approved in China 2021 Oct. and displayed as “2021 CIIE baby”. Commercially launched in Mar 2022, Xultophy® has been written into “Chinese T2DM Guideline (2020 edition)”1.
The product integrates advantages of insulin degludec and liraglutide. Based on dual-receptor and complementary mechanisms of action, the product could effectively achieve up to 89.9% patient at-target rate with less hypoglycemia risk and weight sparring benefits.2~4 The product is once-daily subcutaneous administration at any time of the day and independent of meals.2 Indication in China market is for the treatment of adults with insufficiently controlled T2DM to improve glycaemic control as an adjunct to diet and exercise in addition to other oral medicinal products for the treatment of diabetes.2
参考文献 Reference
1. 中华医学会糖尿病学分会. 中华糖尿病杂志, 2021, 13(4): 315-409.
2. 德谷胰岛素利拉鲁肽注射液说明书(核准日期2021年10月26日)
3. Harris SB, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017 Jun;19(6):858-865
4. Billings LK, et al. Diabetes Care. 2018 May;41(5):1009-1016.
5. Miller E, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019 Dec;21(12):2643-2650.